Blockchain emerges as a modern digital technology solution that emphasizes data security, transparency, and reliability. This technology addresses the challenges of data breaches. Decentralized systems become the main pillar of trust.
The rapid development of digital technology demands strong and adaptive data security systems. Blockchain offers a permanent recording mechanism. Every transaction is protected through advanced cryptography.
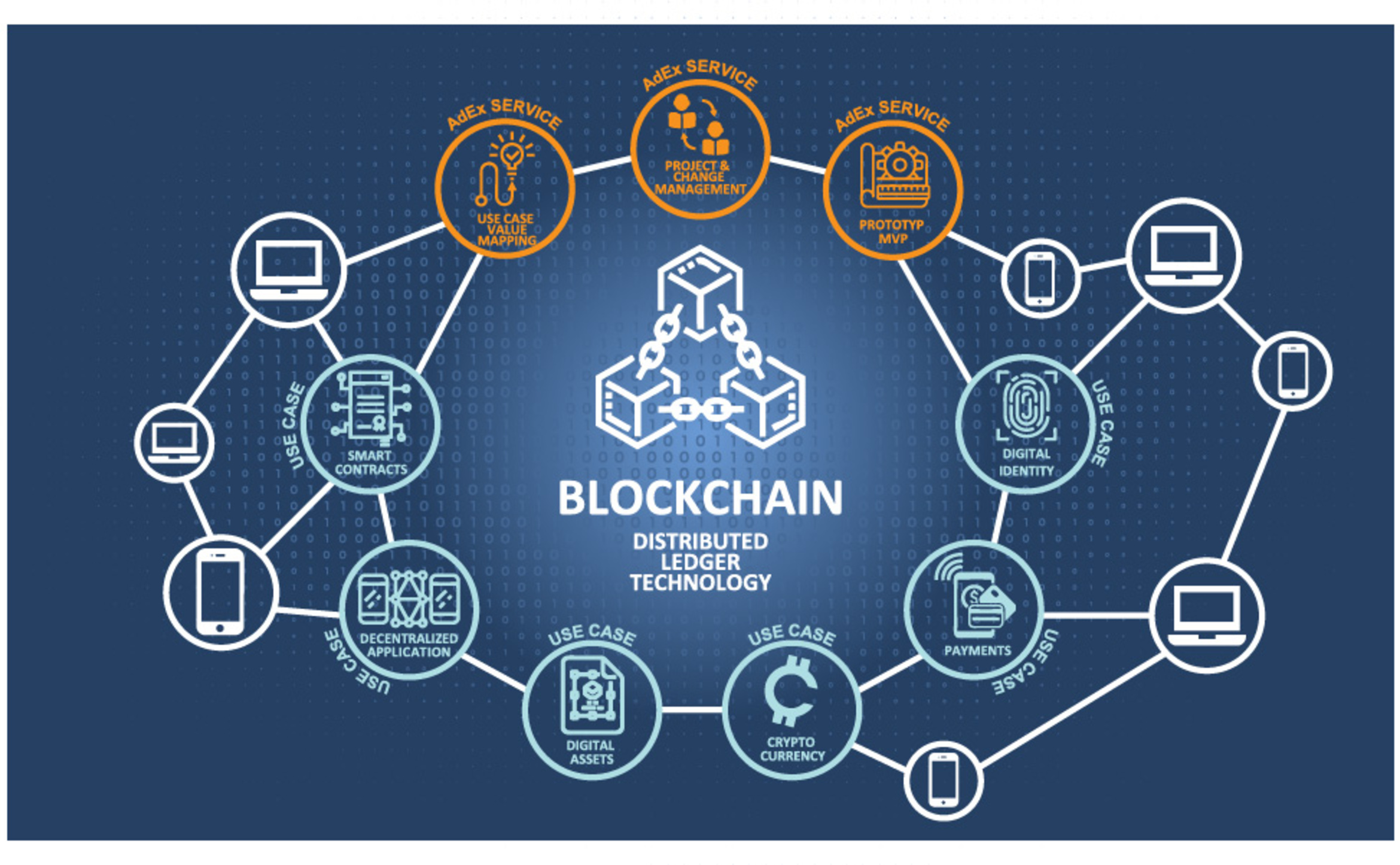
The Role Of Blockchain In Digital Data Security
Blockchain functions as the foundation of digital data security through a distributed and transparent system. This technology eliminates reliance on a single party. Data security increases significantly.
Every piece of data stored on the blockchain is protected by cryptographic mechanisms. Data modification is nearly impossible. This creates a high level of trust among users.
Decentralization becomes the core strength of blockchain in maintaining data integrity. Data is distributed across multiple nodes. The risk of manipulation can be minimized effectively.
Blockchain transaction records are permanent and verifiable. Data history cannot be erased. System transparency supports digital accountability.
With these characteristics, blockchain is adopted across various technology sectors. Data security becomes more assured. Digital transformation runs more securely and stably.
Mechanisms And Implementation Of Blockchain In Data Security
Blockchain operates through technical mechanisms that ensure every data entry is validated before being stored. This process involves a global network. Consensus becomes a crucial element.
1. Block Structure and Data Chain
Blockchain consists of a collection of blocks that are cryptographically linked to one another. Each block stores transaction data. Hashing serves as the main security mechanism.
The linkage between blocks creates a sequential data chain. Any change to a single block affects the entire system. This is what preserves data integrity.
This structure makes blockchain resistant to manipulation. Historical data remains protected. System security increases in multiple layers.
The implementation of block structures supports long term data recording. The system remains consistent. User trust increases over time.
The chained structure allows clear tracking of transaction history. Data becomes easy to audit. The verification process becomes more transparent.
2. The Role of Nodes in Data Verification
Nodes function as computers that maintain the blockchain network. Each node stores a copy of the data. Verification is performed collectively.
The presence of multiple nodes creates a decentralized system. There is no centralized control. The risk of system failure can be reduced.
Nodes verify transactions before they are added to a block. This process ensures data validity. Network consensus determines the final outcome.
Node distribution increases the resilience of the blockchain system. Cyberattacks become difficult to execute. Data security becomes stronger.
The role of nodes also supports transparency in digital systems. Every activity is recorded. Data integrity remains intact.
3. Blockchain Consensus Algorithms
Consensus algorithms regulate how the network agrees on transactions. This method ensures collective agreement. System security is maintained.
Various algorithms are used depending on network requirements. Each method has different characteristics. The goal is to maintain data integrity.
Consensus prevents fraudulent transactions from entering the system. Validation is conducted collectively. Transparency and data reliability increase.
Consensus algorithms reduce the risk of internal manipulation. Decisions are made together. The system becomes fairer and more secure.
Without strong consensus, blockchain becomes unstable. Therefore, this mechanism is critical. Digital security depends on it.
Blockchain utilizes cryptography to secure data. Information is transformed into unique codes. Unauthorized access can be prevented.
Cryptographic hashing ensures that data cannot be altered. Any modification is automatically detected. The system becomes highly sensitive to manipulation.
The use of cryptography increases user trust. Data remains confidential and secure. Digital privacy is preserved.
Cryptography protects data from theft and forgery. Multi layered security systems are formed. The risk of data breaches is significantly reduced.
This technology serves as the foundation of modern blockchain security. Data protection operates consistently. System reliability continues to improve.
5. Transparency in Data Recording
Blockchain creates transparency through open record keeping. Transaction histories can be viewed. Data authenticity is easy to verify.
Transparency does not eliminate data security. Identities remain protected. The system only displays relevant information.
This model increases digital accountability. Every activity is clearly recorded. Trust between parties becomes stronger.
Transparency helps prevent digital fraud. Data can be easily audited. Systems become more honest and open.
Transparent record keeping strengthens the reputation of digital systems. Users feel secure. Public trust increases.
6. Immutability and Long Term Security
Immutability means that blockchain data cannot be altered. Once recorded, data becomes permanent. Long term security is guaranteed.
This characteristic prevents illegal data deletion. Records remain stored. The system becomes more trustworthy.
Immutability supports auditing and data traceability. Information remains consistent. Data validity is preserved.
Long term security is essential for digital systems. Blockchain fulfills this requirement. Data remains secure for years.
This permanent nature strengthens user trust. Manipulation becomes nearly impossible. The system becomes more stable.
Conclusion
Blockchain has become a crucial foundation for data security in modern digital technology. Decentralized and transparent systems increase trust. Data protection operates more optimally.
In the future, blockchain will continue to evolve in response to digital challenges. Innovation and regulation must remain balanced. As a result, digital data security can be sustainably maintained.